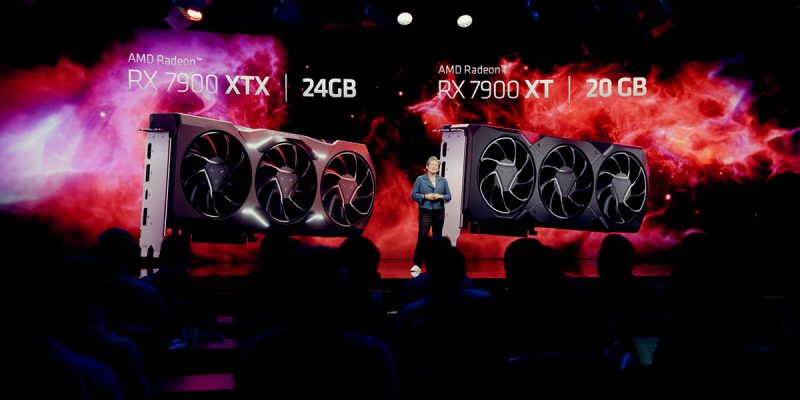
AMD Radeon RX 7900 Series announced: 70% faster, chiplet design from $899
The much-awaited Radeon RX 7000 series from AMD in response to NVIDIA’s GeForce RTX 40 series has finally arrived. Featuring the latest RDNA 3 architecture that is hugely more efficient than RDNA 2, AMD is able to deliver significant performance gains, without an accompanying power draw increase. With a chiplet design, they are also able to hit lower price points than NVIDIA, which is probably the most important factor in these economically dire times. Let’s check them out.
AMD RDNA 3: Faster and more efficient

2.7X higher compute, 70% higher gaming performance

When you check out the specs of the new Radeon RX 7000 series cards later in this article, you might notice that AMD is claiming a pretty huge increase in stream processors. The number of “cores” didn’t actually increase, but AMD is counting it differently. Each “core” can now handle two instructions per cycle, which provides for faster performance, as long you have enough parallel instructions to go with it. So that’s in an ideal scenario, where you can get 2.6X the FP32 throughput out of the Radeon RX 7900 XTX versus the Radeon RX 6950 XT.
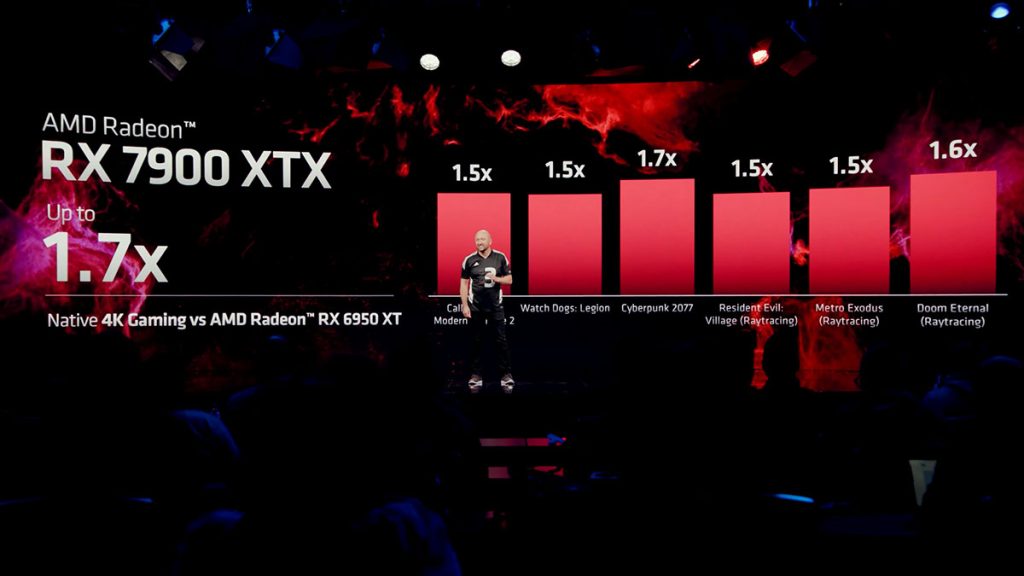
When it comes to gaming, which is not going to be as perfect a situation for the GPU, the gains are more modest at around 70%. This is still a very impressive gain, and definitely nothing to scoff at. If AMD is able to get developers on their side to take advantage of the way RDNA 3 is designed, we might even see greater leaps in performance. But of course, that’s like betting on unhatched eggs.
Up to 54% better efficiency than RDNA 2

After NVIDIA’s 600W connector-burning fiasco, this probably makes for the best headline. In any case, while AMD is still bumping up the power draw rating by 20W from last year’s Radeon RX 6950 XT, the raised efficiency will also mean that you are going to see much better performance here. Interestingly enough, part of this efficiency boost comes from decoupling the shader clocks from the front end, which allowed for higher max frequencies and 25% power savings.
Chiplet design for better more cost-effectiveness

Chiplets changed the game for AMD in their CPU business, allowing them to strike Intel in every segment. Just like their CPUs, the chiplets in RDNA 3 are manufactured on different nodes to maximize cost effectiveness. By manufacturing the Graphics Compute Die (GCD) on the 5nm node, AMD gets to enjoy all the efficiency, density and performance perks of TSMC’s newer node. Meanwhile the Memory Cache Die (MCD), which doesn’t scale as well with the latest node, can be manufactured on the older 6nm node.
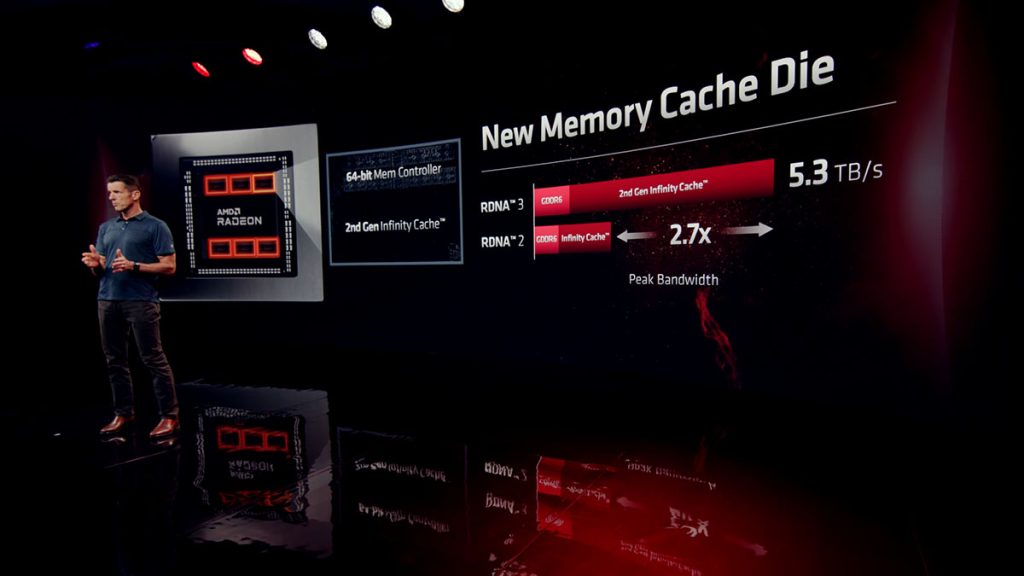
The MCD hosts the memory controller as well as the Infinity Cache, with the flagship Radeon RX 7900 XTX featuring six active MCDs, for a 384-bit memory bus and 96MB of 2nd Gen Infinity Cache. This new Infinity Cache has a max bandwidth of 5.3TB/s, 2.7x faster than what was in RDNA 2. The total size is also smaller than what we saw with the flagship AMD RDNA 2 GPUs, which can come with up to 128MB Infinity Cache. However AMD is confident that they managed to increase the cache hit rate, thus increasing performance despite the smaller capacity.
New AI Accelerators and 2nd Gen Ray Accelerators

While NVIDIA and Intel have proven the merits of AI-accelerated upscaling, it seems that AMD is finally joining the party. AMD is claiming that their new AI Accelerators in the Radeon RX 7900 XTX bring 2.7X the AI performance of the Radeon RX 6950 XT, which doesn’t have dedicated hardware to handle it. Worth noting is that AMD’s FidelityFX Super Resolution has yet to take advantage of AI, AMD will probably be releasing something down the line to take advantage of the new AI Accelerators in RDNA 3. Will this get as much hate from confused gamers as DLSS 3? Well, time will tell.

RDNA 2 was also rather weak when it comes to raytracing performance, usually ending up slower than NVIDIA Ampere offerings from a tier below. RDNA 3 might still see a distinct gap between NVIDIA and AMD’s raytracing chops, but at least things are improving in the red camp. AMD is claiming up to 1.5X more rays in flight, which results in around a 47% to 84% increase in raytracing performance, at least according to AMD.
New Radiance Display engine and dual media engine

AMD will be the first to adopt DisplayPort 2.1, with NVIDIA peculiarly leaving it out of their Ada Lovelace lineup. They even came up with a nice fancy name for it: AMD Radiance Display Engine. With support for DisplayPort 2.1, gamers can get 2X the bandwidth of DisplayPort 1.4, which will translate to higher resolutions and higher refresh rates, all the way up to 8K 165Hz or 1440p 900Hz. There’s also 12-bit color, expanding the support to 68 billion colors, up from 10-bit’s 1.08 billion.

What I think is more interesting the new media engine though. This addresses yet another weakness in AMD’s lineup, which is their video encoder. When comparing AMF to NVENC, no sane streamer or creator will tell you to go with AMD. Hopefully, this will improve things. RDNA 3’s new dual media engines is now reportedly 80% faster than RDNA 2’s and can handle simultaneous encoding and decoding of H.265 streams. AV1 encode and decode support is also here, bringing AMD up to parity with Intel and NVIDIA offerings.
AMD Radeon RX 7000 Series starts from $899

The first salvo from AMD will feature two cards, the Radeon RX 7900 XT and Radeon RX 7900 XTX. Last year’s Radeon RX 6900 XT was launched at $999, and AMD decided not to rock the boat. The Radeon RX 7900 XT will start from $899, while the Radeon RX 7900 XTX will go for $999. Overall, the Radeon RX 7900 series look quite promising. They are more affordable than NVIDIA’s offerings, which should help to entice gamers to jump to the red camp, if they are willing to brave AMD’s notoriously buggy drivers. Personally, I do look forward to AMD’s take on AI upscaling after trying to pass FSR off as the equivalent of DLSS for two years.
AMD Radeon RX 7000 Series Specs and Price
| AMD Radeon RX 7900 XT | AMD Radeon RX 7900 XTX | |
| GPU | Navi 31(?), TSMC 5nm 10,752 Stream Processors 84 Ray Accelerators (2nd Gen) 168 AI Accelerators | Navi 31(?), TSMC 5nm 12,288 Stream Processors 96 Ray Accelerators (2nd Gen) 192 AI Accelerators |
| Boost Clocks | 2.4GHz | 2.5GHz |
| Performance | 103 TFLOPs FP16 52 TFLOPs FP32 | 123 TFLOPs FP16 61 TFLOPs FP32 |
| Memory | 96MB Infinity Cache (2nd Gen) 20GB GDDR6 (20Gbps) 320-bit memory bus | 96MB Infinity Cache (2nd Gen) 24GB GDDR6 (24Gbps) 384-bit memory bus |
| Interface | PCIe 4.0 x16 | PCIe 4.0 x16 |
| TGP rating | 300W | 355W |
| Price | $899 | $999 |
| Availability | 13th December 2022 | 13th December 2022 |