Blood Pressure Machines Accuracy: Huawei Watch D2 vs Cuff vs Sphygmomanometer
As we review the Huawei Watch D2, a question arises: How accurate are its blood pressure readings?

On hand, we have two other blood pressure measurement tools: an Automatic Cuff-Based Blood Pressure Monitor and the Huawei Watch D2. Since all 2 devices are MDA-approved, any discrepancies in readings could lead to confusion.
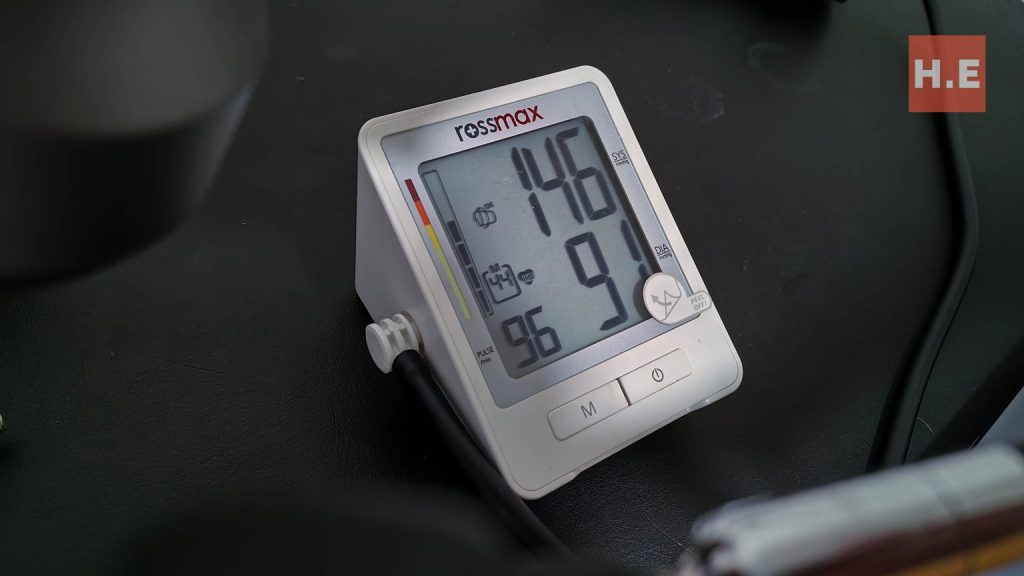

To ensure the accuracy of the Huawei Watch D2’s blood pressure readings, especially considering the potential life-or-death implications of inaccurate blood pressure measurements, we consulted with a medical professional.
We spoke to Dr Pearl, a GP that runs her own clinic in hartamas to shed light on this matter and provide expert guidance.
Understanding the Blood Pressure Basics
Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against your artery walls. It’s measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is typically written as two numbers:
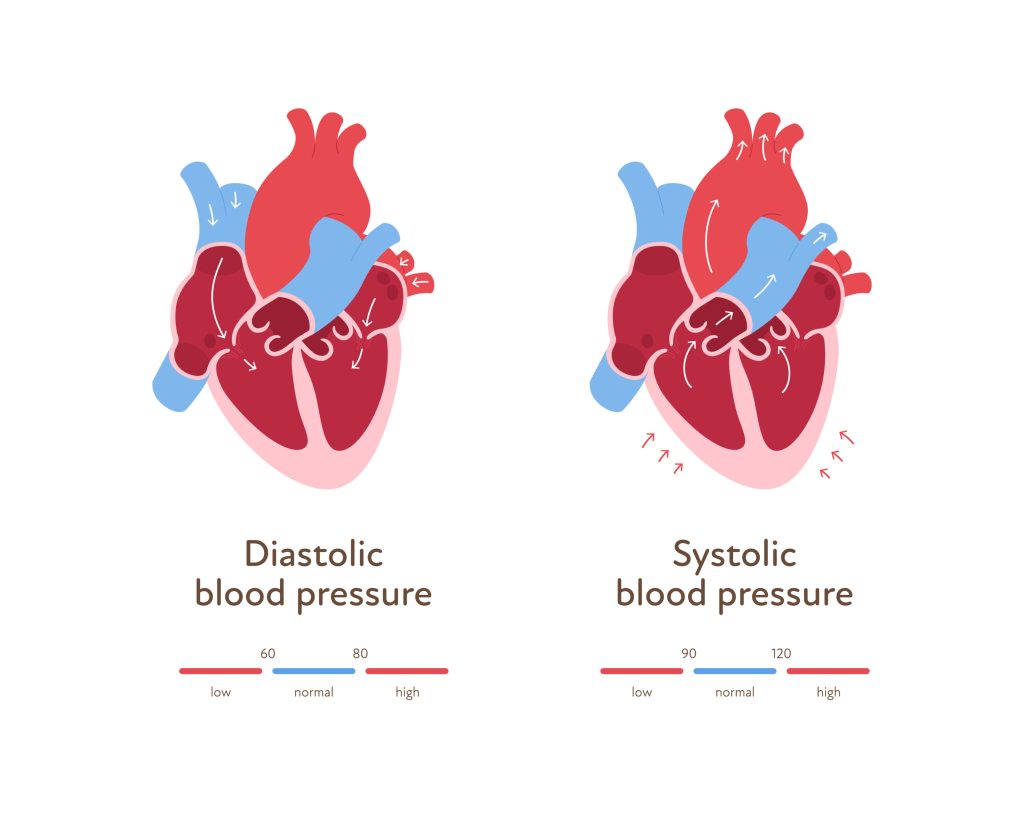
- Systolic Pressure: The top number, which measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats.
- Diastolic Pressure: The bottom number, which measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart rests between beats.
Why is Blood Pressure Important?
High blood pressure, or hypertension, can damage your blood vessels over time, leading to serious health problems like heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. Regular monitoring of your blood pressure is crucial for early detection and management of hypertension.
Understanding Blood Pressure Readings
Here’s a breakdown of different blood pressure categories:
| BLOOD PRESSURE CATEGORY | SYSTOLIC mm Hg (upper number) | and/or | DIASTOLIC mm Hg (lower number) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NORMAL | LESS THAN 120 | and | LESS THAN 80 |
| ELEVATED | 120 – 129 | and | LESS THAN 80 |
| HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE (HYPERTENSION) STAGE 1 | 130 – 139 | or | 80 – 89 |
| HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE (HYPERTENSION) STAGE 2 | 140 OR HIGHER | or | 90 OR HIGHER |
| HYPERTENSIVE CRISIS (consult your doctor immediately) | HIGHER THAN 180 | and/or | HIGHER THAN 120 |
Factors Affecting Blood Pressure
Several factors can influence your blood pressure, including:

- Age: Blood pressure tends to increase with age.
- Family History: A family history of high blood pressure can increase your risk.
- Lifestyle: Factors like diet, exercise, stress, and smoking can impact your blood pressure.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease or diabetes, can contribute to high blood pressure.
- Medications: Some medications can raise or lower blood pressure.
Types of Blood Pressure Monitors
There are primarily three types of blood pressure monitors available:
Sphygmomanometer Blood Pressure Monitors:
A sphygmomanometer, often referred to as a manual blood pressure monitor, is a device used to measure blood pressure. It consists of an inflatable cuff, a pressure gauge, and a stethoscope.
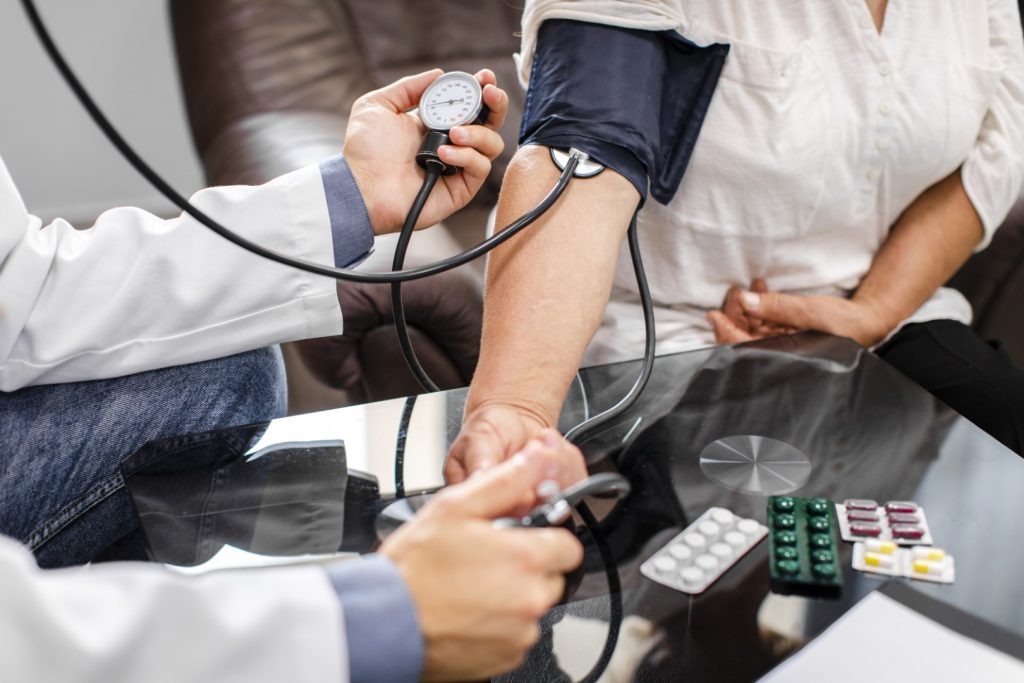
How it Works: A healthcare professional inflates the cuff around your upper arm to a pressure higher than your systolic blood pressure. They then slowly release the pressure while listening to your blood flow with a stethoscope. The pressure at which the first sound is heard is the systolic pressure, and the pressure at which the sound disappears is the diastolic pressure.
Pros: Highly accurate when used by a trained professional. Can be used in various settings.
Cons: Requires training and skill, time-consuming, not suitable for home use by most people.
Automatic Cuff-Based Blood Pressure Monitors:
These devices use an electronic cuff that automatically inflates and deflates, measuring your blood pressure.

How it Works: The cuff is placed around your upper arm, and the device uses sensors to detect your blood pressure. The results are displayed on a digital screen.
Pros: Easy to use, provides consistent readings, suitable for home use.
Cons: Can be less accurate in certain situations (e.g., irregular heart rhythms), may require larger cuffs for some people.
Huawei Watch D2/ Wrist Blood Pressure Monitors:
These Smart watch/ devices use a smaller cuff that is placed around your wrist.
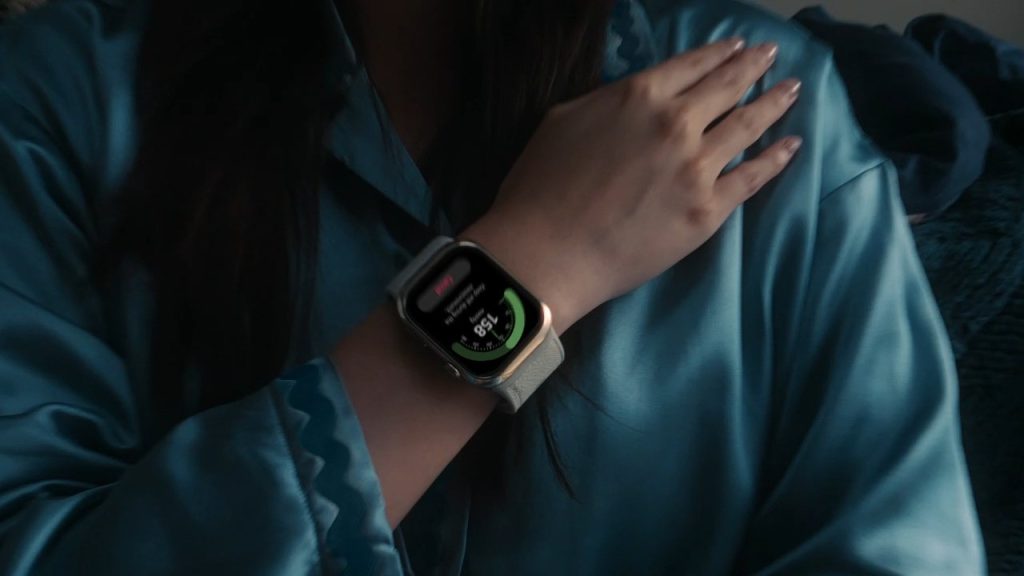

How it Works: The cuff is inflated and deflated, and the device measures your blood pressure. The results are displayed on a digital screen. Wrist blood pressure monitors, such as the Huawei Watch D2, are wearable devices that measure blood pressure directly from your wrist.
How it Works: The device uses advanced sensors to detect blood pressure by emitting pulses of light and analyzing the reflected light. This technology allows for non-invasive and continuous blood pressure monitoring.
Pros: Portable and convenient, highly efficient to be used for frequent monitoring. Often have dual function, doubling as a fully functional smart watch. In the case of Huawei Watch D2, its includes capable of monitoring six major systems, including the cardiovascular, respiratory, nervous, endocrine, reproductive, and muscular health systems.
Cons: Requires careful positioning of the wrist, can be affected by movement and temperature, less accurate than other methods.
A Real-World Comparison
To gain firsthand insights into the accuracy and reliability of different blood pressure measurement methods, I underwent a series of tests with Dr. Pearl. We used all three methods mentioned above: Sphygmomanometer, Automatic Cuff-Based Blood Pressure Monitors, and Huawei Watch D2/Wrist Blood Pressure Monitors.
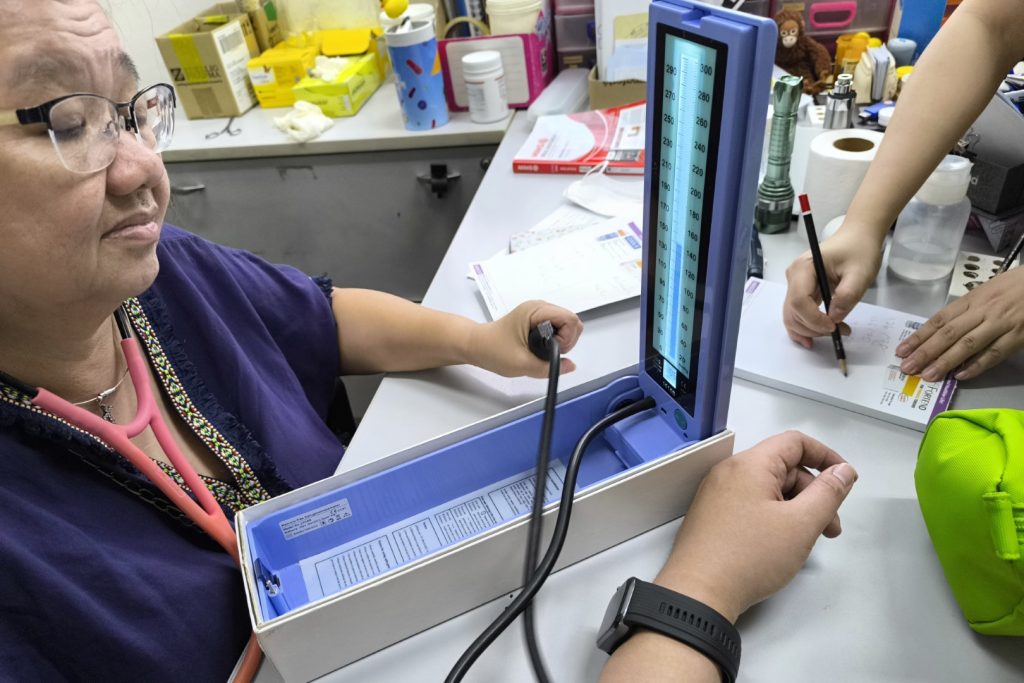
Dr. Pearl emphasized that instead of relying on a single reading, it’s crucial to look for stable and consistent readings from at least two measurements.
Here are the readings we obtained:
| Sphygmomanometer | Huawei Watch D2 | Automatic Cuff-Based Blood Pressure Monitors | |
| 1st Reading | 115/70 | 126/78 | 110/75 |
| 2nd Reading | 114/74 | 126/75 | 124/71 |
| 3rd Reading | 119/76 | ||
| 4th Reading | 117/74 | 112/69 | |
| 5th Reading | 117/65 | ||
| Average | 115/72 | 122/76 | 116/70 |
While the cuff-based monitor produced an outlier reading (170/52), it was removed from the result. All results were combine together and formed an average.
The Result
As you can see, the Huawei Watch D2’s results are slightly higher than the others. However, these results are still considered accurate. Several studies have shown that wrist-based blood pressure monitors can provide reliable readings, though they may be slightly higher than those obtained from traditional arm-based devices.

Dr. Pearl emphasized that consistent patterns in blood pressure readings are more important than individual measurements. By tracking these patterns over time, we can gain valuable insights into our overall health and identify potential issues early on.
To learn more about continuous blood pressure monitoring, or Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM), check out our dedicated article below.
Key Takeaways:
- Consistency is Key: Rather than relying on a single reading, it’s essential to monitor your blood pressure over time and identify patterns.
- Device Accuracy: All three methods can provide accurate readings when used correctly. However, manual methods, when performed by a trained professional, are often considered the gold standard.
- Home Monitoring: Automatic cuff-based monitors are suitable for home use and can help you track your blood pressure regularly.
- Consult Your Doctor: Regularly consult your healthcare provider to discuss your blood pressure readings and receive personalized advice.
By understanding the different types of blood pressure monitors and following these guidelines, you can effectively manage your blood pressure and take proactive steps towards a healthier life.
For the full review of the Huawei Watch D2, check out our comprehensive review above.













Hi, against the national health the pressure readings with this watch are 20 % higher on the systolic reading, this has been substantiated by 3 tests by the nhs , as I’m high level diabetic I have tests on a regular basis